In the fast-paced world of emerging technologies, we come across various terms. Getting exposed to such a wide range of information is overwhelming sometimes and we often get confused about the actual meaning of those terms. One such term is Virtualization.
Before moving on to the technical definition, we would start with an analogy to comprehend better. Let us take an example of public transport say a bus. If public transports were not present, each passenger traveling via that bus would use their own vehicle to travel. This would waste resources and increase the vehicle count on the roads, which may result in more traffic jams. So instead of using so many vehicles, a bus would do the same amount of work much better efficiently. The introduction of public transport systems saved us a lot of resources compared to every passenger driving their own vehicle.
Virtualization is like the Public Transportation Authority, where the physical host is a bus and virtual machines are the passengers of this bus. The maintenance also become much easier as instead of maintaining and repairing all the vehicles, only one bus has to be repaired. This would save both time and resources.
What is Virtualization?
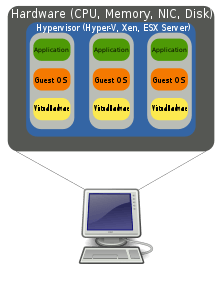
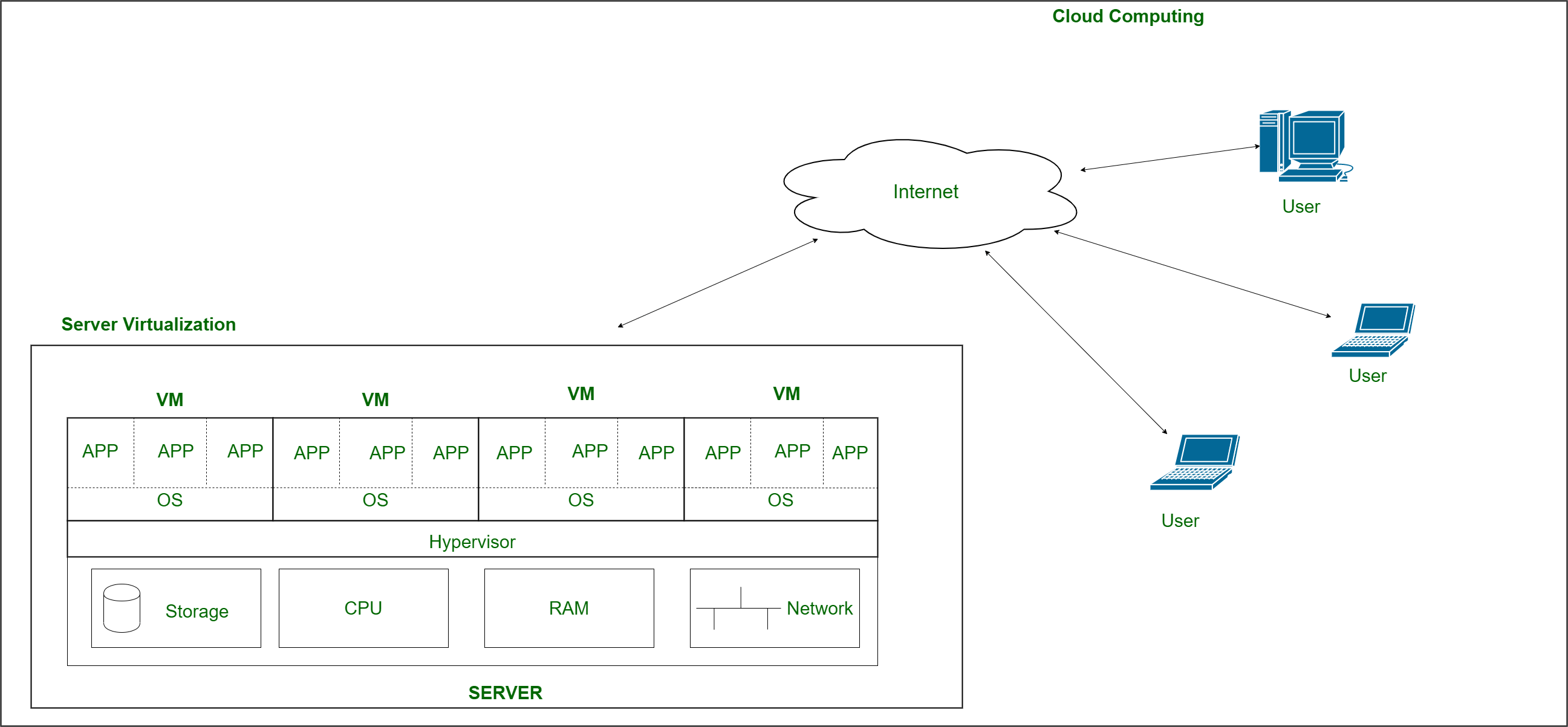
Virtualization is the creation of a virtual (not actual) version of something, such as a server, a desktop, a storage device, an operating system, or network resources. With the help of Virtualization, multiple operating systems and applications can run on the same machine concurrently, increasing the utility and flexibility of hardware. It allows you to use a physical machine’s full capacity by distributing its capabilities among many users or environments. Virtual Machines are a virtual representation of a physical computer. Each Virtual Machine works independently.
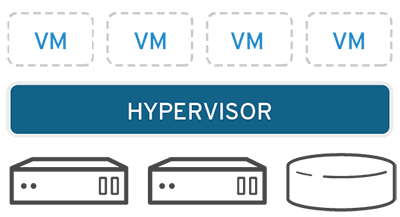 In the picture above you can get a brief idea of how virtualization is performed. There is a software called Hypervisor that separates the physical resources from the virtual environments. Hypervisors help to use more of a system’s available resources and provide greater IT mobility since the guest virtual machines are independent of the host's physical machine. Resources are partitioned as needed from the physical environment to the virtual environments created.
In the picture above you can get a brief idea of how virtualization is performed. There is a software called Hypervisor that separates the physical resources from the virtual environments. Hypervisors help to use more of a system’s available resources and provide greater IT mobility since the guest virtual machines are independent of the host's physical machine. Resources are partitioned as needed from the physical environment to the virtual environments created.
Brief History of Virtualization
The history of virtualization dates back to the 1960s but it was not popular by then. Although the technologies that enabled virtualization like hypervisors were developed decades ago to give multiple users simultaneous access to computers that performed batch processing when during the 1990s companies had physical servers capable of executing a single task at a time. Thus the resources remained underused. This is where virtualization really took off. It was the natural solution to 2 problems: companies could partition their servers and run apps on multiple operating system types and versions.
Types Of Virtualization
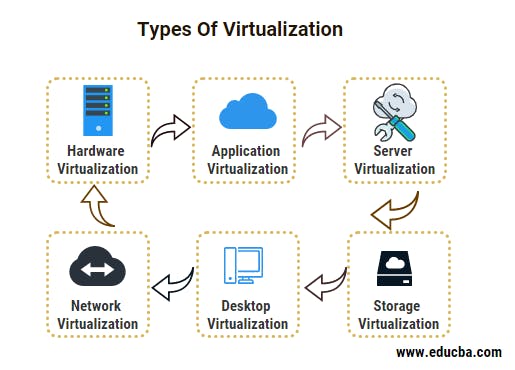
Hardware Virtualization
Virtualization of the entire computer as a hardware system is called hardware virtualization. It is achieved by abstracting the physical hardware layer by using a hypervisor. Hardware virtualization is mainly done for the server platforms because controlling virtual machines is much easier than controlling a physical server. Using or modifying the virtual hardware does not affect the physical hardware. It hides the physical characteristics of the computing platform.
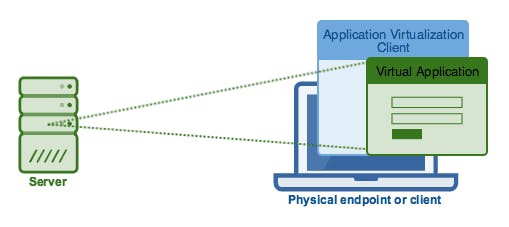
Application Virtualization
Application virtualization software allows users to access and use an application remotely. It means the user can access and utilize the application from any other computer other than the one on which the application is installed. The application can run on the local workstations of the users.
Server Virtualization
Server virtualization is the process of splitting a physical server into multiple unique and isolated virtual servers by using a software application. Each virtual server can run its own operating systems independently.
Network Virtualization
Network Virtualization can combine multiple physical networks into one virtual, software-based network, or it can divide one physical network into separate, independent virtual networks.
Desktop Virtualization
It means virtualizing the user workstation so it can be accessed from a remotely connected device from any location. Users who want a specific OS other than Windows Server will need to have a virtual desktop. Desktop virtualization promotes portability, mobility, and ease of management.
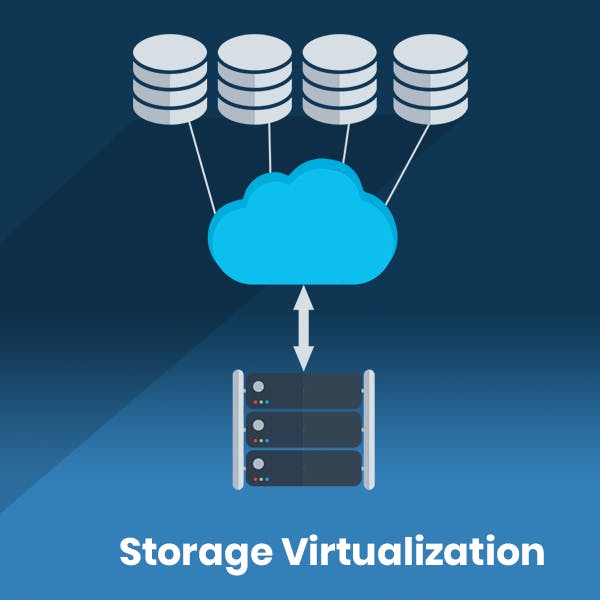
Storage Virtualization
Virtual storage application is a software alternative to traditional hardware-based storage. Physical storage is virtualized to form multiple virtual storages thus increasing the availability and saving cost. The downtime gets significantly reduced and loss of data can be prevented as data is distributed in various virtual storage devices.
Why Virtualization?
- Reduce IT expenses
- Increase efficiency and productivity
- Reduce downtime and enhance resiliency in disaster recovery situations
- Provides independent environments for individual users
So I hope you found this article helpful and informative. Do Like, Share and Comment with your thoughts.